Describe the Subcutaneous Layer and Its Functions
The subcutaneous hypodermis layer is a specialized layer of connective tissue containing adipocytes. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Skin General Functions Structure Anatomy Epidermis Layers Cells
The subcutaneous layer also.
. Stores fat cells for energy reserves Gives the body its smooth contoured appearance Regulates temperature through the contraction and dilation of blood vessels Serves as the attachment point for bones muscles and other organs to the skin Contains deep pressure sensors. Also called adipose or subcutis tissue. Describe the functions of the epidermis.
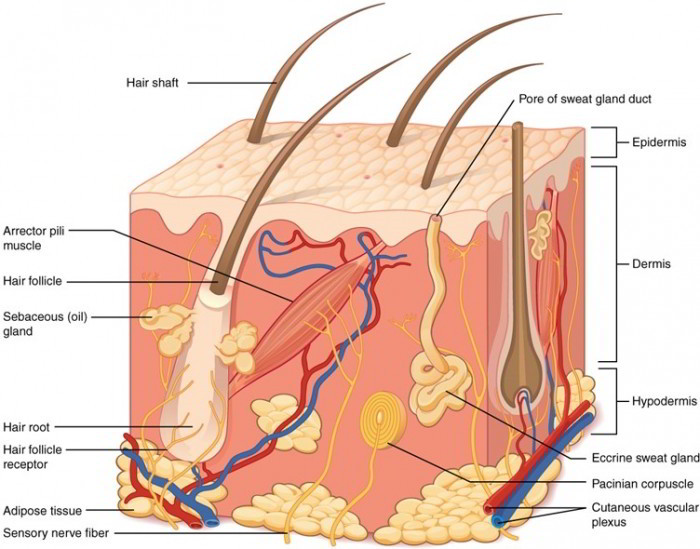
Structure of the skin. The subcutaneous layer is also an important line of defense protecting the fragile organs and bones from outside forces such as pathogens. With respect to the epidermis.
List the structural layers of the epidermis and describe their functions. Often it has large amounts of adipose tissue and it may contain the deeper elements of sweat glands as well as sensory receptors. Its the layer of skin where fat is deposited and stored.
The hypodermis is made of subcutaneous under the skin fats connective tissues blood vessels and nerve cells. It consists of mostly adipose tissue and is the storage site of most body fat. Indicate the tissue types that compose the epidermis dermis and subcutaneous layer of skin.
It consists primarily of areolar connective tissue and adipose tissue. The subcutaneous layer of skin houses the arterioles that regulate temperature and also acts as a layer for fat storage a shock absorber and as insulation. Hypodermis Subcutaneous Tissue Your hypodermis is the bottom layer of skin in your body.
The skin performs a variety of functions. Explain how each of the five layers as well as each of the following cell types and. The hypodermis is deep to the dermis and is also called subcutaneous fascia.
The hypodermis subcutaneous layer or superficial fascia lies between the dermis and underlying tissues and organs. This narrow multilayered structure anchors the epidermis to the dermis. It also does a good job at retaining water and important nutrients in the skin.
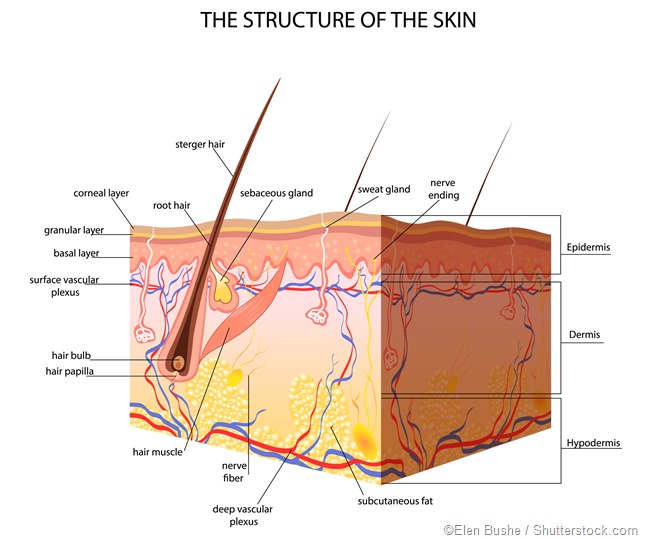
Outer most is stratum corneum statum lucidum statum granulosum stratum spinosum and statum basale from outer most to innerside. The subcutaneous tissue superficial fascia in gross anatomy anchors the skin to underlying tissues. Explain the structure and function of the stratum corneum.
Roles of specific tissue layers of skin the subcutaneous layer a. It is the site used for subcutaneous injections and where white blood cells attack pathogens that have penetrated the skin. How does this relate to the continuous growth self-regeneration of the epidermis.
Its important to take care of your epidermis. The epidermis is composed mainly of keratinocytes. The epidermis is composed of four main strata or layers.
Although technically not part of the skin the hypodermis subcutaneous layer or superficial fascia lies beneath the dermis. It has many important functions including protecting your body from the outside world keeping your skin hydrated producing new skin cells and determining your skin color. Identify and describe the dermis and its layers including the tissue types making up each dermal layer.
Define the skin as an organ and a component of the integumentary system. The subcutaneous layer is primarily made up of fat and connective tissue. It is the deepest layer of skin and contains adipose lobules along with some skin appendages like the hair follicles sensory neurons and blood vessels.
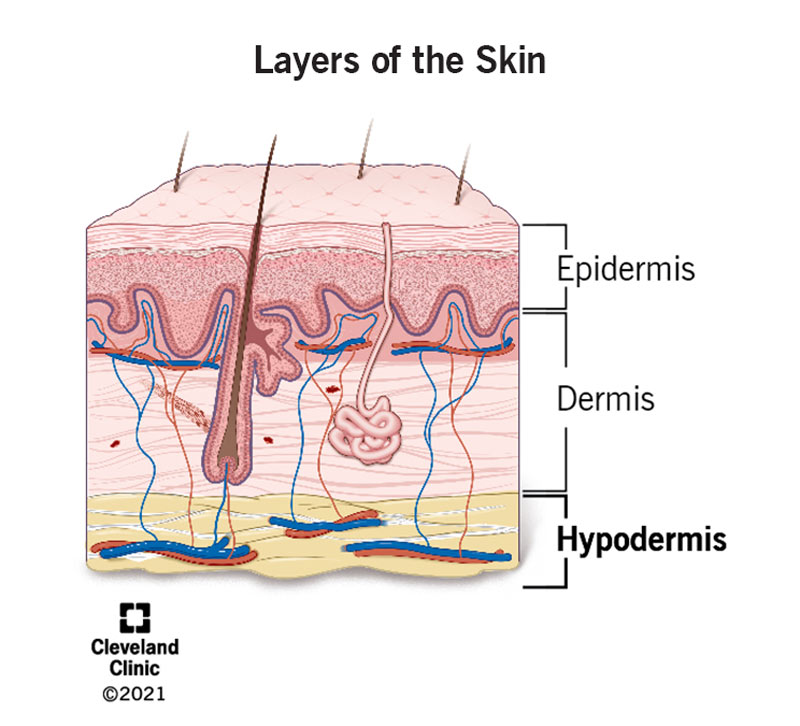
Subcutaneous tissue Fatty layer found below the dermis that gives smoothness and contour to the body contains fat for use as energy and also acts as a protective cushion for the outer skin. The subcutaneous tissues serve four functions regulating body temperature is key The subcutaneous layer also serves to protect the inner organs and bones and plays an important role in. The skin is divided into several layers as shown in Fig 1.
It has many functions including insulating your body protecting your body from harm storing energy and connecting your skin to your muscles and bones. Explain how the skin is structurally divided into epidermal dermal and subcutaneous regions. The skin consists of two layers the epidermis and the underlying dermis.
Describe the general functions of the subcutaneous layer also known as the hypodermis or superficial fascia. Name and describe the 4 layers of epidermis. How does it differ in thick vs.
It provides a barrier from the outside world defending against harmful foreign substances and pathogens from entering the deeper layers of skin and our bodys bloodstream. The blood vessels in the hypodermis are bigger and connect to the rest of your body. Beneath the epidermis is the basement membrane also known as the dermo-epidermal junction.
Based on the thickness of the epidermal layer only skin is classified as thick or thin. Protection is provided against biological invasion physical damage and ultraviolet radiation. List the functions of the integumentary system.
Identify and describe the tissue type making up the epidermis. The fat insulates the body against both heat and cold while the blood vessels and nerves woven throughout it help to regulate temperature.
Hypodermis Subcutaneous Tissue Function Structure

Function And Structure Of Skin And Subcutaneous Tissue Earth S Lab
No comments for "Describe the Subcutaneous Layer and Its Functions"
Post a Comment